
Long-term weight loss is never accomplished through a crash diet; similarly, academic improvement is never accomplished through a temporary fix. Real change happens when action toward improvement is ongoing. Benchmarking and progress monitoring should be a consistent part of teachers’ and students’ lives.
Over the years, Response to Intervention (RTI) has developed into a comprehensive “lifestyle” approach to student progress monitoring. In the beginning, RTI looked like the well-known Response to Intervention pyramid. This pyramid was divided into student tiers, where each tier received its own specialized intervention “diet.” Later, this structure began to incorporate not only academic intervention
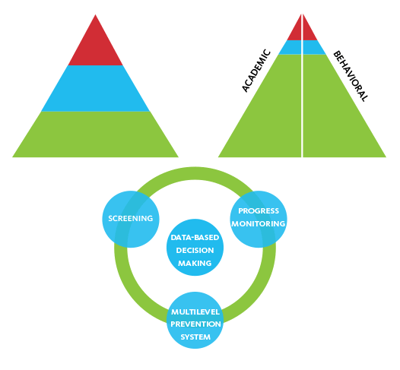
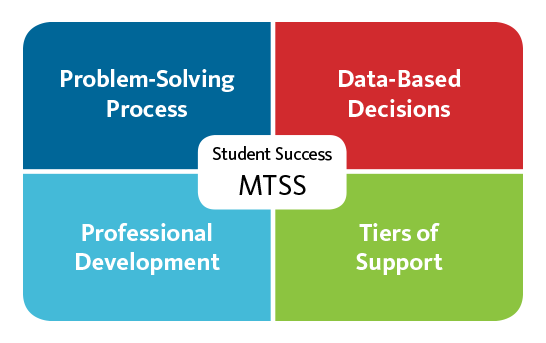
As RTI grew even more in scope and depth, intervention and support started to further incorporate the diverse needs of students. The RTI pyramid model morphed into a circle to represent ongoing student intervention, also known as Multi-Tier System of Supports (MTSS). In addition, the behavioral aspects of intervention came to include cultural awareness, evidence-based practices, and a multilevel prevention system that incorporated things such as a school’s community and MTSS technologies.
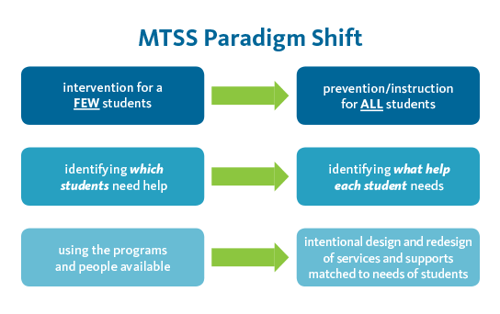
The terms RTI and MTSS are not interchangeable. It is important to understand that RTI fits within the MTSS framework. MTSS is a more extensive system of student intervention that involves not only a heightened community awareness but also a greater focus on prevention for all students, not just those who are struggling.
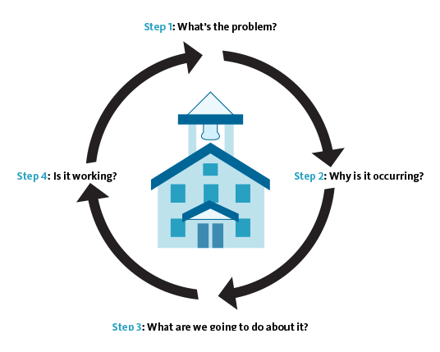
RTI focuses on providing high-quality instruction and intervention to struggling students, typically students in Tier 3. Assessment, progress monitoring, and data-driven decision making are all part of successful RtI implementation. RtI helps prevent students from going into Special Ed while challenging them within their specific instruction.
RtI falls within the greater MTSS structure, which involves the entire school system in the intervention process. MTSS is multi-tier, meaning that it provides support to all students, from struggling students to advanced learners. MTSS makes sure resources such as technology tools, effective curriculum, and Professional Development A professional development team provides tools and training for Istation software and services. are provided to empower teachers, to support staff, and ultimately, to help students.
MTSS addresses not only students’ academic performance, but also their social, emotional, and behavioral development. It fosters increased collaboration between special and general education, as well as between the school district, teachers, and administrators. Finally, MTSS puts a greater emphasis on prevention than it does
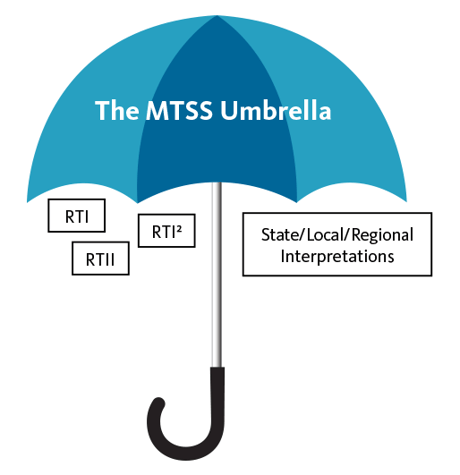
Various intervention models exist under MTSS, including RtI, RtI², and many more. Each district has its own MTSS/RTI model based on what works best for its community.
The RtI² framework is a component of core instruction that is three-pronged with student achievement at the center:
In general, RTII is a comprehensive three-tier standards-aligned strategy to enable early identification and intervention for students who may be at risk of academic or behavioral problems. The overarching goal of RTII is to improve student achievement using research-based interventions matched to the instructional need and level of each student.
RTII uses the prevention model to prevent academic and behavioral problems in schools. RTII is the intersection of two federal laws, NCLB and IDEA 200, and helps ensure that all students are proficient readers by the end of 3rd grade.
Progress monitoring is used to assess a student’s academic performance, to quantify a student’s rate of improvement or responsiveness to instruction, and to evaluate the effectiveness of instruction. One can monitor the progress of individual students or an entire class.
When progress monitoring, it is important to ensure fidelity of implementation and to select evidence-based tools with regard to cultural and linguistic responsiveness and student strengths.
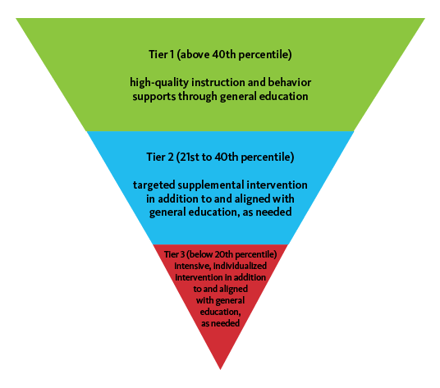
Student tiers help to deliver differentiated instruction to students based on their level of difficulty with particular subject matter. There are three tiers of instructional processes, although some models discuss a fourth tier and other models divide the tiers into smaller units.
The Tier 1 instructional program is identified with the core curriculum, which is typically aligned with state standards. This curriculum delivers instruction that has established known outcomes for general education. All students receive Tier 1 instruction, but students who are struggling with the core curriculum receive additional instruction at Tier 2 or Tier 3.
Tier 2 students fall below the expected levels of accomplishment (called benchmarks) and are at some risk of academic failure, but they are still above levels that indicate a high risk of failure. The needs of these students are identified through the assessment process, and instructional programs are delivered that focus on their specific needs. Instruction is provided in small groups instead of the larger classroom setting.
Tier 3 students are at high risk of failure. Students in Tier 3 are usually put into even smaller groups (three to five students). Some models use one-to-one instruction. Tier 3 includes students whose needs are at the intensive level.
Istation focuses on differentiation for all students, not just intervention for struggling students. Our digital platform, acting as a supplemental tool for instructors, is well suited for the blended learning classroom. Istation also offers thousands of hours of easily accessible Teacher Resources for whole-group, small-group, and/or one-on-one intervention.
If you want to get the most out of your classroom intervention practices, optimize your efforts with effective blended learning support from Istation.
Istation’s computer-adaptive curriculum and assessments have the essentials schools need to personalize learning.
Istation’s all-inclusive essentials are currently helping over four million students grow!
Offering support to families in the community is a great way to bolster support for extending learning beyond the typical school day. Oak Grove Elementary School in Florida started doing this by connecting with students’ parents and working with local libraries to set up instructional time for extra practice. Providing parents access to educational resources in their homes and around the community accelerated literacy growth.
Istation’s Priority Reports show students’ strengths as well as the areas in which they need extra practice. These reports provide guidance when leading small groups or one-on-one interventions. There are teacher directed lessons (TDLs) associated with each skill shown on the Priority Report. Having these resources available can save time in gathering materials for intervention efforts.
Delivering powerful results while ensuring equity and reducing teacher workload, Istation’s educational technology meets the needs of all students – at school and at home. Contact us to learn how to build your intervention team with Istation.
5214F Diamond Heights Blvd., San Francisco, California 94131